FDA advisors back Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine for young kids
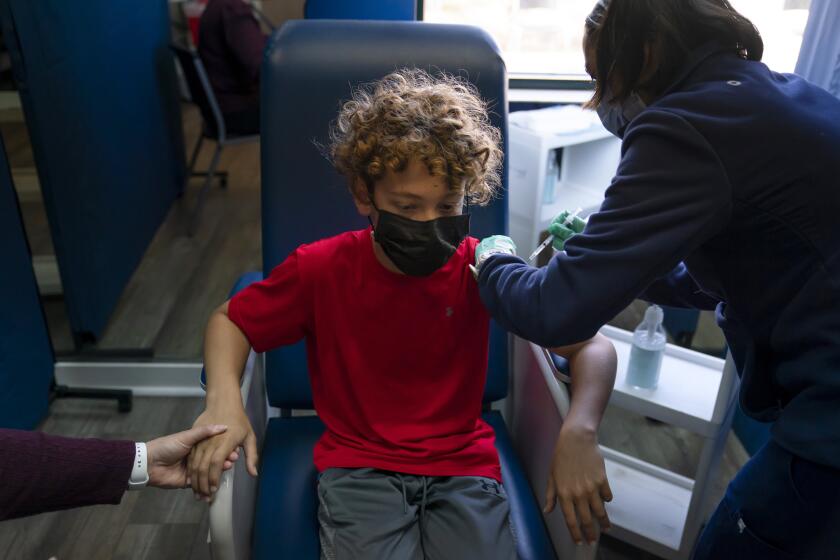
A panel of U.S. health advisers endorsed kid-size doses of Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine, moving the country closer to beginning vaccinations for children ages 5 to 11.
- Share via
WASHINGTON — The U.S. moved a step closer to expanding COVID-19 vaccinations for millions more children as a panel of government health advisors on Tuesday endorsed kid-size doses of the shots made by Pfizer and BioNTech for children ages 5 to 11.
A Food and Drug Administration advisory panel voted unanimously with one abstention that the vaccine’s benefits in preventing COVID-19 in that age group outweigh any potential risks — including a heart-related side effect that’s been very rare in teens and young adults who get a much higher dose.
While children are at lower risk of severe COVID-19 than older people, many panelists ultimately decided it’s important to give parents the choice to protect their youngsters — especially those at high risk of illness or who live in places where other precautions, like masks in schools, aren’t being used.
The virus is “not going away. We have to find a way to live with it, and I think the vaccines give us a way to do that,” said FDA advisor Jeannette Lee of the University of Arkansas.
“I do think it’s a relatively close call,” said advisor Dr. Eric Rubin of Harvard University. “It’s really going to be a question of what the prevailing conditions are, but we’re never going to learn about how safe this vaccine is unless we start giving it.”
The FDA isn’t bound by the panel’s recommendation and is expected to make its own decision within days.
If the FDA authorizes the kid-size doses, there’s still another step: Next week, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention will have to decide whether to recommend the shots and which youngsters should get them.
With the Delta variant surging, pediatricians and others are urging the FDA to move faster on COVID-19 vaccines for young children.
Full-strength shots made by Pfizer and BioNTech already are recommended for everyone 12 and older, but pediatricians and many parents are clamoring for protection for younger children. The extra-contagious Delta variant has caused an alarming rise in pediatric infections — and families are frustrated with school quarantines and having to say no to sleepovers and other rites of childhood to keep the virus at bay.
States are getting ready to roll out shots for little arms — in special orange-capped vials to distinguish them from the adult version of vaccine — as soon as the government gives the OK. More than 25,000 pediatricians and other primary care providers have signed up so far to offer vaccination.
While there is less COVID-19 among 5- to 11-year-olds, they still have faced substantial illness — including more than 8,300 hospitalizations reported. About a third of those patients required intensive care, and nearly 100 died.
Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine for children as young as 5 could be available by early November at pharmacies and pediatrician’s offices.
A study of elementary schoolchildren found the Pfizer shots were nearly 91% effective at preventing coronavirus infections with COVID-19 symptoms — even though the youngsters received just a third of the dose given to teens and adults.
Pfizer’s study tracked 2,268 children ages 5 to 11 who got two shots three weeks apart of either a placebo or the dose for kids. Vaccinated youngsters developed levels of virus-fighting antibodies just as strong as those in teens and young adults who got the full-strength shots.
And so far, 16 kids given dummy shots developed COVID-19 compared with three vaccinated youngsters. Most of the study data were collected in the U.S. during August and September, as the Delta variant surged.
The kid dosage also proved safe, with similar or fewer temporary side effects — such as sore arms, fever or achiness — than teens experience. At the FDA’s request, Pfizer more recently enrolled an additional 2,300 youngsters into the study, and preliminary safety data have shown no red flags.
The study isn’t large enough to detect any extremely rare side effects, such as the heart inflammation that occasionally occurs after the second dose, mostly in young men and teen boys.
The Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine greatly reduced the risk of coronavirus infection and COVID-19 in teens despite the Delta variant’s rise.
Statistical models developed by FDA scientists showed that in most scenarios of the continuing pandemic, the vaccine would prevent far more COVID-19 hospitalizations in this age group than would potentially be caused by heart inflammation.
But with cases falling across the U.S., the FDA panel had to consider whether the pandemic might recede so much that more children could face side effects from the vaccine than would be protected from COVID-19.
“If the trends continue the way they are going, then the emergency for children is not what we might think it might be,” said Dr. James Hildreth of Meharry Medical College.
Moderna also is studying its vaccine in young children, and Pfizer has additional studies underway in those younger than 5.