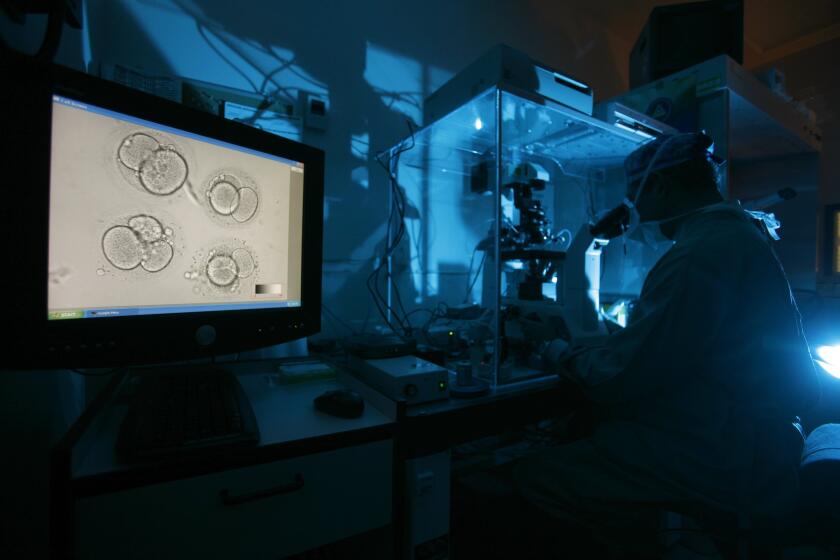
A second Alabama IVF provider cuts back services after court ruling on frozen embryos

- Share via
MONTGOMERY, Ala. — A second in vitro fertilization provider in Alabama paused parts of its treatment Thursday, sending patients scrambling to make other plans after the state Supreme Court ruled that frozen embryos are legally considered children.
Alabama Fertility Services said in a statement that it has “made the impossibly difficult decision to hold new IVF treatments due to the legal risk to our clinic and our embryologists.”
The decision comes a day after the University of Alabama at Birmingham health system said in a statement that it was pausing IVF treatments so it could evaluate whether its patients or doctors could face criminal charges or punitive damages.
“We are contacting patients that will be affected today to find solutions for them and we are working as hard as we can to alert our legislators as to the far-reaching negative impact of this ruling on the women of Alabama,” Alabama Fertility said. “AFS will not close. We will continue to fight for our patients and the families of Alabama.”
Doctors and patients have been grappling with shock and fear this week as they try to understand what they can and can’t do after the ruling by the all-Republican Alabama Supreme Court that raises questions about the future of IVF.
Alabama Fertility Services’ decision left Gabby Goidel, who was days from an expected egg retrieval, calling clinics across the South looking for a place to continue IVF care.
The Alabama Supreme Court has ruled that frozen embryos created during fertility treatments should be considered children under state law.
“I freaked out. I started crying. I felt in an extreme limbo state. They did not have all the answers. I did not obviously have any answers,” Goidel said.
The Alabama ruling came down Friday, the same day Goidel began a 10-day series of injections ahead of egg retrieval, with the hopes of getting pregnant through IVF next month. Goidel, who has experienced three miscarriages and turned to IVF as a way for she and her husband to fulfill their dream of becoming parents, found a place in Texas that will continue her care and plans to travel there Thursday night.
“It’s not pro-family in any way,” Goidel said of the Alabama ruling.
Dr. Michael C. Allemand, a reproductive endocrinologist at Alabama Fertility, said Wednesday that IVF is often the best treatment for patients who desperately want a child, and the ruling threatens doctors’ ability to provide that care.
“The moments that our patients are wanting to have by growing their families — Christmas mornings with grandparents, kindergarten, going in the first day of school, with little backpacks — all that stuff is what this is about. Those are the real moments that this ruling could deprive patients of,” he said.
Dr. Brett Davenport, a doctor at Fertility Institute of North Alabama, posted a video to social media Wednesday urging his patients to not panic, saying that IVF care would continue.
An L.A. couple have sued Fujifilm Irvine Scientific, alleging the company’s mineral oil used in the IVF process destroyed their embryos.
“We are still going to perform IVF as we always have,” Davenport said in the video.
Justices — citing language in the Alabama Constitution that the state recognizes the “rights of the unborn child” — said three couples could sue for wrongful death when their frozen embryos were destroyed in an accident at a storage facility.
“Unborn children are ‘children’ ... without exception based on developmental stage, physical location, or any other ancillary characteristics,” Justice Jay Mitchell wrote in Friday’s majority ruling. Mitchell said the court had previously ruled that a fetus killed when a woman is pregnant is covered under Alabama’s Wrongful Death of a Minor Act and nothing excludes “extrauterine children from the Act’s coverage.”
Although the Alabama court case centered on whether embryos were covered under the wrongful death of a minor statute, some said treating the embryo as a child could have broader implications.
Rachel Rebouche, dean of Temple University’s Beasley School of Law in Philadelphia, sees the ruling as “emblematic of the long march toward fetal personhood.”
“This may not be the case that launches it, but this is a very strategic decision on the part of antiabortion forces because they know that personhood bills have failed,” Rebouche said.
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.